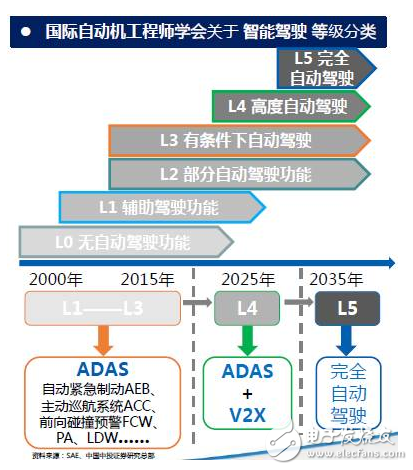
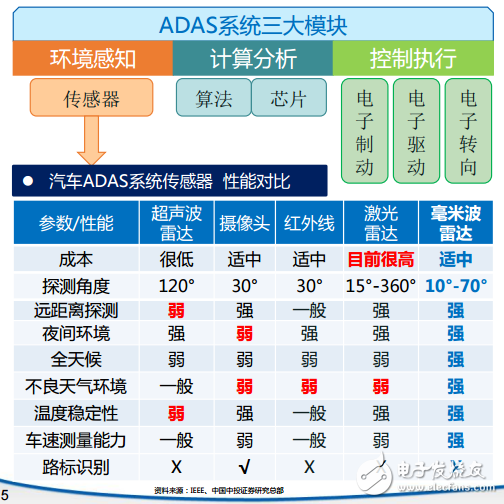
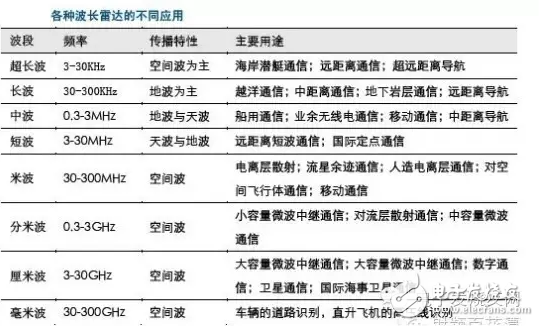
Even if you haven't heard of ADAS yet, you will not be unfamiliar with automatic driving. With Google and Baidu's self-driving cars on the road, many people are also looking forward to this technology. However, most of the cars are still in the stage of popularization of ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance System) applications, in which the millimeter wave radar has to be mentioned. The International Society of Automated Engineers divides the level of intelligent driving into five levels, and we are currently in the ADAS stage. The popularization of ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistant System) is the first condition for the realization of unmanned driving in the future, and is the technical basis for improving the active safety performance of automobiles. The ADAS system is divided into three modules: environment awareness, computational analysis, and control execution. Among them, the sensor plays an important role in the environment sensing module. A variety of sensor fusion applications are inevitable trends in the future, and the millimeter wave radar will be the first to become the main sensor of the ADAS system. So what is the millimeter wave radar? Generally, an electromagnetic wave having a wavelength of 1 to 10 mm is called a millimeter wave, which is located in a wavelength range in which microwaves and far infrared waves overlap, and has the following four characteristics: Extremely wide bandwidth: The millimeter wave frequency range is generally considered to be 26.5 to 300 GHz and the bandwidth is as high as 273.5 GHz. More than 10 times the total bandwidth from DC to microwave. Even considering atmospheric absorption, only four main windows can be used for propagation in the atmosphere, but the total bandwidth of the four windows is also up to 135 GHz, which is five times the sum of the bandwidths of the bands below the microwave. This is undoubtedly very attractive today when the frequency resources are tight. • Beam narrow: The millimeter wave beam is much narrower than the microwave beam at the same antenna size. For example, a 12 cm antenna has a beam width of 18 degrees at 9.4 GHz and a wave speed width of only 1.8 degrees at 94 GHz. It is therefore possible to distinguish small targets that are closer together or to see the details of the target more clearly. • Compared to lasers: the propagation of millimeter waves is much less affected by the climate and can be considered to have all-weather characteristics. • Compared to microwaves: Millimeter wave components are much smaller. Therefore, the millimeter wave system is easier to miniaturize. Because the millimeter wave radar has the characteristics of small size, easy integration and high spatial resolution compared to the centimeter wave radar. Early applied to the military field, with the development and advancement of radar technology, millimeter wave radar sensors began to be used in many fields such as automotive electronics, drones, and intelligent transportation. Vehicle-mounted millimeter-wave radars operate at frequencies of 24 GHz and 77 GHz, and a few countries (such as Japan) use the 60 GHz band. 6-10HP Compressor Series Sealed Terminal Blocks 6-10Hp Compressor Series Sealed Terminal Blocks,D Type Terminal For Compressor,Three-Phase Seal Terminal For Home Appliance,Air Conditioner Compressor Terminals With Rubber Shenzhen Capitol Micro-Electronics Co.,LTD , https://www.capitolgtms.com