The damping coefficient of the power amplifier is a relatively important indicator of the power amplifier. It is a relative value. It is a relative value because it is closely related to the impedance of the load. In the strict sense, it is also related to frequency. The parameter of the damping coefficient is calculated as the ratio of the load impedance to the internal resistance. Theoretically, the larger the damping coefficient of the power amplifier, the stronger the control ability for the load, and the smaller the damping coefficient, the weaker the control ability of the load. But it only represents the resistance coefficient, which follows the above rules for the same load. However, different loads (speakers) have different physical damping forces, so the larger the damping coefficient, the better the concept is not completely correct, because it does not necessarily apply to all loads (the physico-mechanical damping coefficients of different loads are different). In theory, the larger the damping coefficient of the power amplifier, the stronger the control ability of the load. First we analyze what changes the damping coefficient, the internal resistance of the power amplifier, and the load impedance. The larger the damping coefficient, the better the concept is not completely correct, because it does not necessarily apply to all loads. Assuming that the line resistance between the load and the power amplifier is 0.1 ohm, the voltage obtained at both ends of the load is calculated by the formula in the common state of the wire and the load. First calculate the loss voltage of the wire: Powersoft X Series Variable Damping Control The above calculation results show that the influence of the wire on the damping coefficient of the power amplifier is very large. SDEC 401-999KW Diesel Generator Perkins 401-999Kw Diesel Generator,Perkins Shanghai Genset,Perkins Shanghai Power Generator,401-999Kw Diesel Generator Shanghai Kosta Electric Co., Ltd. , https://www.generatorkosta.com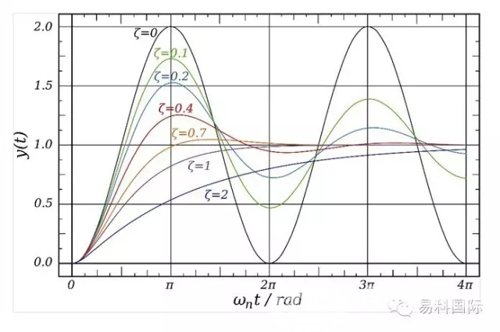
The formula we usually use is Rs=Rt(Vo/Vt-1)
Rs indicates that the internal resistance of the power amplifier Rt indicates the equivalent resistance of the terminal connected to the output terminal. Vo indicates that the open output voltage of the power amplifier Vt indicates the voltage across the terminal resistor. The formula calculates the internal resistance of the power amplifier by the circuit principle, and then calculates the resistance through the ratio of the load to the internal resistance. Nie coefficient. Changing the damping coefficient principle of the power amplifier does not change the internal resistance parameter (the value of the internal resistance is determined by the entire circuit structure and working mode after the power amplifier design is completed, and the value is a physical fixed value), but the voltage reaching the load position in the closed state is changed. Usually, the wire loses a part of the voltage during the transmission, and the length of the wire causes the internal resistance of the power amplifier to increase. Therefore, it causes a reduction in the resistance coefficient and affects the serious consequences of the low frequency control force. The following analysis is performed by calculation:
Assume that our equivalent load impedance is 8 ohms, and the open-circuit output voltage of the measuring power amplifier is 8V. When all states are unchanged, the load of 8 ohms is added (the load is directly connected to the output of the power amplifier, there is no intermediate wire loss), and both ends of the load The voltage is 7.99V, we calculate the internal resistance of the amplifier by the formula:
Rs=Rt(Vo/Vt-1)
Rs=8(8/7.99-1)
Rs=0.01
The internal resistance of the power amplifier is 0.01, the equivalent impedance of the load is 8 ohms, and the resistance coefficient of the power amplifier under offline state is 800. This value is theoretical under the condition that there is no wire. However, in practical applications, the wire must be used as the carrier between the power amplifier and the speaker load. In fact, it should not be ignored. The influence of the impedance of the wire on the voltage and damping coefficient is calculated by the following formula. According to Ohm's law R=U/I, R is the resistance, U is the voltage, I is the current, and the parameter is calculated by the formula to put the current in the current state:
R=U/I
8=7.99/I
I=0.99875
The theoretical operating current of the power amplifier under the load of 8 ohms is calculated to be 0.99875 amps. 
R=U/I
0.1=U/0.99875
U=0.099875
Calculate the wire loss voltage is 0.099875V, and subtract the line loss voltage 0.099875V from the ideal wireless damage voltage 7.99V. The voltage obtained at both ends of the load is 7.890125V when the wire and load are in common state.
Through the formula, the resistance coefficient of the wire and the load in the common state can be calculated. We calculate the internal resistance of the power amplifier in the current state by the formula:
Rs=Rt (Vo/Vt-1)
Rs=8.1 (8/7.890125-1)
Rs=0.1142
The internal resistance of the power amplifier is 0.1142, and the equivalent impedance of the load is 8.1 ohms. By calculating the common state of the wire and the load, the resistance coefficient of the power amplifier is 72. 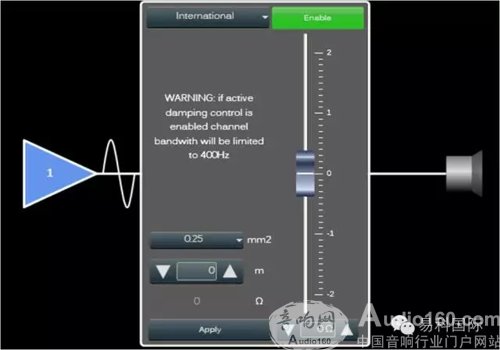
Through the above analysis, it can be seen that Powersoft's variable damping coefficient function is very important. The power amplifier fully considers the problem that the loss of the wire damages the damping coefficient and affects the control load capacity.
The working principle of the amplifier is as follows: the power amplifier hardware architecture must have a digital product with closed-loop detection function, and adjust the damping coefficient of the power amplifier by controlling the output voltage difference between the open circuit and the closed circuit. Input the parameters of the wire (line length and wire diameter or wire impedance), the power amplifier software automatically increases the closed circuit output voltage according to the input wire impedance parameter, so as to maintain the line loss state, the load application end obtains an effective high resistance coefficient. Features. The above is the basic principle of the variable damping coefficient of Powersoft power amplifier. 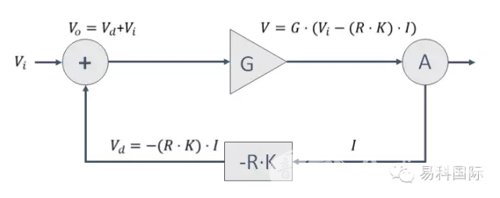
Powersoft Variable Damping Control Link