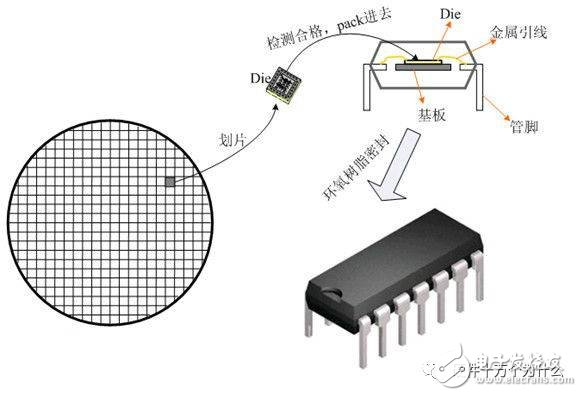
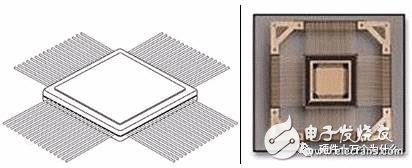
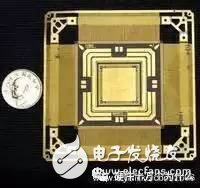
Package, Package, is the process of assembling an integrated circuit into the final product of the chip. Simply put, the integrated circuit die (Die) produced by Foundry is placed on a substrate that carries the load, and the pin is led out. Then fix the package into a whole. As a verb, "package" emphasizes the process and action of placing, fixing, sealing, and leading; as a term, "package" mainly focuses on the form, category, substrate and outer casing, and lead material, emphasizing its protection chip and enhancing electric heating. Performance, easy to assemble the important role of the machine. 1. The ratio of chip area to package area is to improve package efficiency, as close as possible to 1:1; 2, the pin should be as short as possible to reduce the delay, the distance between the pins as far as possible to ensure mutual interference, improve performance; 3. Based on the requirements of heat dissipation, the thinner the package, the better. The package is mainly divided into DIP dual in-line and SMD chip package. In terms of structure, the package has experienced the earliest transistor TO (such as TO-89, TO92) package developed into a dual in-line package, and then PHILIP company developed a small SOP package, and later derived SOJ (J type) Pin small outline package), TSOP (thin small outline package), VSOP (very small outline package), SSOP (reduced SOP), TSSOP (thin reduced SOP) and SOT (small outline transistor), SOIC (small outline) Integrated circuit) and so on. From the material medium, including metals, ceramics, plastics, many high-strength working conditions, such as military and aerospace grades, still have a large number of metal packages. 1, BGA package (ball grid array) One of the spherical contact display, surface mount packages. A spherical bump is formed on the back surface of the printed substrate in place of the lead, and the LSI chip is mounted on the front surface of the printed substrate, and then sealed by a molding resin or a potting method. Also known as a bump display carrier (PAC). The pin can exceed 200 and is a package for multi-pin LSI. The package body can also be made smaller than the QFP (four-sided pin flat package). For example, a 360-pin BGA with a 1.5mm center-to-center lead is only 31mm square; a 304-pin QFP with a 0.5mm center-to-center distance is 40mm square. And BGA doesn't have to worry about pin deformation like QFP. The package was developed by Motorola Inc. of the United States and was first adopted in devices such as cellular phones, and is likely to become popular in personal computers in the United States in the future. Initially, the BGA has a pin (bump) center-to-center distance of 1.5mm and a pin count of 225. There are also some LSI manufacturers that are developing 500-pin BGAs. The problem with BGA is the visual inspection after reflow soldering. It is not clear whether an effective visual inspection method is available. Some believe that due to the large center distance of the weld, the connection can be considered stable and can only be handled by functional inspection. The Motorola Company of the United States refers to the package sealed with molded resin as OMPAC, and the package sealed by the potting method is called GPAC (see OMPAC and GPAC). 2, BQFP package (quad flat packagewith bumper) Quad flat-lead package with pad. One of the QFP packages has protrusions (cushions) at the four corners of the package body to prevent bending deformation of the pins during shipping. US semiconductor manufacturers use this package primarily in circuits such as microprocessors and ASICs. The center of the pin is 0.635mm and the number of pins is from 84 to 196 (see QFP). 3, butt joint pin grid array (butt joint pin grid array) Another name for surface mount PGA (see surface mount PGA). 4, C- (ceramic) package Indicates the mark of the ceramic package. For example, CDIP stands for ceramic DIP. It is a mark that is often used in practice. 5, Cerdip package A glass-sealed ceramic dual in-line package for an ECL RAM, DSP (digital signal processor) circuit and the like. Cerdip with glass window It is used for UV erase type EPROM and internal microcomputer circuit with EPROM. The center of the pin is 2.54mm and the number of pins is from 8 to 42. In Japan, this package is indicated as DIP-G (G is the meaning of a glass seal). 6, Cerquad package One of the surface mount packages, the bottom sealed ceramic QFP, is used to package logic LSI circuits such as DSP. Cerquad with a window is used to encapsulate the EPROM circuit. The heat dissipation is better than that of plastic QFP, which can be tolerated under natural air cooling conditions. 5 to 2W of power. But the cost of packaging is better than plastic QFP is 3 to 5 times higher. The center distance of the pins is 1.27mm, 0.8mm, 0.65mm, 0.5mm, 0.4mm and other specifications. The number of pins is from 32 to 368. A ceramic chip carrier with a lead, one of the surface mount packages, with leads drawn from the four sides of the package in a T-shape. A window-mounted package for UV-erasing EPROMs and microcomputer circuits with EPROMs. This package is also known as QFJ, QFJ-G (see QFJ). 7, CLCC package (ceramic leadedchip carrier) A ceramic chip carrier with a lead, one of the surface mount packages, with leads drawn from the four sides of the package in a T-shape. A window-mounted package for UV-erasing EPROMs and microcomputer circuits with EPROMs. This package is also known as QFJ, QFJ-G (see QFJ). 8, COB package (chip on board) The chip- on-board package is one of the bare chip mounting technologies. The semiconductor chip is placed on the printed circuit board. The electrical connection between the chip and the substrate is realized by the wire stitching method. The electrical connection between the chip and the substrate is realized by the wire stitching method. Resin coverage to ensure compatibility. Although COB is the simplest bare chip placement technology, its packaging density is far less than TAB and rewind soldering technology. 9, DFP (dual flat package) Double-sided pin flat package. It is another name for SOP (see SOP). I used to have this method before, but now I have basically not used it. 10, DIC (dual in-line ceramic package) Another name for ceramic DIP (including glass seal) (see DIP). 11, DIL (dual in-line) Another name for DIP (see DIP). European semiconductor manufacturers use this name more. 12, DIP (dual in-line package) dual in-line package. One of the plug-in packages, the leads are led out from both sides of the package, and the package materials are plastic and ceramic. DIP is the most popular plug-in package, and its application range includes standard logic IC, memory LSI, and microcomputer circuit. The pin center is 2.54mm apart and the number of pins is from 6 to 64. The package width is typically 15.2mm. Some packages with widths of 7.52mm and 10.16mm are called skinny DIP and slim DIP (narrow body DIP). However, in most cases, it is not differentiated and is simply referred to as DIP. In addition, ceramic DIP sealed with low melting glass is also known as cerdip (see cerdip). 13, DSO (dual small out-lint) Double-sided pin small outline package. Another name for SOP (see SOP). Some semiconductor manufacturers use this name. 14, DICP (dual tape carrier package) Double-sided pin-loaded package. One of TCP (loaded package). The leads are fabricated on the insulating tape and pulled out from both sides of the package. Due to the TAB (Automatic On-Load Soldering) technology, the package is very thin. It is commonly used in liquid crystal display driver LSIs, but most of them are fixed products. In addition, a 0.5mm thick memory LSI booklet package is in the development stage. In Japan, DICP is named DTP according to the EIAJ (Japan Electromechanical Industry) standard. 15, DIP (dual tape carrier package) Ibid. The name of DTCP is standard by the Japan Electromechanical Industry Association (see DTCP). 16, FP (flat package) Flat package. One of the surface mount packages. Another name for QFP or SOP (see QFP and SOP). Some semiconductor manufacturers use this name. 17, Flip-chip Reverse soldering chips. One of the bare chip packaging technologies is to form metal bumps in the electrode regions of the LSI chip, and then bond the metal bumps to the electrode regions on the printed substrate. The footprint of the package is essentially the same as the chip size. It is the smallest and thinnest of all packaging technologies. However, if the thermal expansion coefficient of the substrate is different from that of the LSI chip, a reaction occurs at the joint, thereby affecting the reliability of the connection. Therefore, it is necessary to reinforce the LSI chip with a resin and use a substrate material having substantially the same thermal expansion coefficient. The SiS 756 North Bridge is available in the latest Flip-chip package and fully supports the AMD Athlon 64/FX central processor. Support PCI Express X16 interface, providing graphics card up to 8GB / s two-way transmission bandwidth. Supports the highest HyperTransport Technology with a transmission bandwidth of up to 2000MT/s MHz. Built-in SiS Technology exclusive AdvancedHyperStreaming Technology, MuTIOL 1G Technology. 18, FQFP (fine pitch quad flat package) The small pin center is from the QFP. Usually refers to a QFP with a pin pitch less than 0.65mm (see QFP). Some conductor manufacturers use this name. The package form of the PQFP (Plastic Quad Flat Package) PQFP is the most common. The distance between the chip pins is very small, the pins are very thin, and many large-scale or large integrated circuits are used in this package form, and the number of pins is generally more than 100. The 80286, 80386 and some 486 motherboard chips in the Intel family of CPUs are available in this package. Chips in this package must be soldered to the board using SMT technology (surface mount equipment). Chips mounted using SMT technology do not have to be perforated on the board. Typically, solder joints of the corresponding pins are designed on the surface of the board. The soldering to the motherboard can be achieved by aligning the legs of the chip with the corresponding solder joints. Chips soldered in this way are difficult to disassemble without special tools. SMT technology is also widely used in the field of chip soldering, and many advanced packaging technologies have required SMT soldering. The following is a 286 processor chip in AMD's QFP package. 0.5mm weld zone center distance, 208 I/O pins, external dimensions 28×28mm, chip size 10×10mm, chip area/package area=10×10/28×28=1:7.8, This shows that the QFP is much smaller than the DIP package size. PQFP packaged motherboard sound card chip 19. CPAC (globetop pad array carrier) Another name for BGA in the US Motorola company (see BGA). 20, CQFP military wafer lithographic package (CeramicQuad Flat-pack Package) The wafer on the right is a military chip package (CQFP), which is what the package did before it was placed in the crystal. This package is only available in military products and aerospace industrial wafers. There is a thick gold compartment next to the wafer slot (higher, not visible on the photo) to prevent radiation and other interference. Screw holes are provided on the periphery to secure the wafer to the motherboard. The most interesting is the gold-plated pins around, which greatly reduces the thickness of the chip package and provides excellent heat dissipation. 21, H-(with heat sink) Indicates a mark with a heat sink. For example, HSOP stands for SOP with a heat sink. 22, Pin Grid Array (Surface Mount Type) Surface mount PGA. Usually the PGA is a cartridge type package with a lead length of approximately 3.4 mm. The surface mount PGA has a display-like pin on the underside of the package, ranging in length from 1.5mm to 2.0mm. The mounting method is a method of bump welding with a printed substrate, and is therefore also referred to as a bump-welded PGA. Because the pin center distance is only 1.27mm, which is less than half of the plug-in type PGA, the package body can be made not very large, and the pin count is more than the plug-in type (250~528), which is used for large-scale logic LSI. Package. The packaged substrate has a multilayer ceramic substrate and a glass epoxy printing base. Packaging with a multilayer ceramic substrate has been put to practical use. PGA package Weigang mini DDR333 memory 23, JLC package (J-leaded chip carrier) J-shaped pin chip carrier. Refers to the window CLCC and the ceramic QFJ with window (see CLCC and QFJ). The name adopted by some semiconductor manufacturers. 24, LCC package (Leadless chip carrier) Leadless chip carrier. Refers to the surface mount package with no electrodes on the four sides of the ceramic substrate. It is a package for high speed and high frequency ICs, also known as ceramic QFN or QFN-C (see QFN). 25, LGA package (land grid array) Contact display package. That is, a package having an array state electrode contact is fabricated on the bottom surface. Plug in the socket when assembling. A practical ceramic LG with 227 contacts (1.27mm center distance) and 447 contacts (2.54mm center distance) is now available for high speed logic LSI circuits. Compared to QFP, LGA can accommodate more I/O pins in a smaller package. In addition, since the impedance of the lead is small, it is suitable for high-speed LSI. However, due to the complexity of the socket production and the high cost, it is basically not used very much now. It is expected that its demand will increase in the future. AMD's 2.66GHz dual-core Opteron F Santa Rosa platform 26, LOC package (lead onchip) 26, on-chip lead package One of the LSI package technologies, the front end of the lead frame is a structure above the chip, and a bump is formed near the center of the chip, and is electrically connected by wire bonding. The chip accommodated in the same size package has a width of about 1 mm compared to the structure in which the lead frame is originally disposed near the side of the chip. Hitachi Metals Introduces 2.9mm Square 3-Axis Accelerometer 27, LQFP package (low profile quadflat package) Thin QFP. Refers to the QFP with a package body thickness of 1.4mm, which is the name used by the Japan Electromechanical Industry Association according to the new QFP form factor. 28, L-QUAD package One of the ceramic QFPs. The package substrate is made of aluminum nitride, and the base thermal conductivity is 7 to 8 times higher than that of alumina, and has good heat dissipation properties. The packaged frame is made of alumina, and the chip is sealed by potting, thereby suppressing cost. It is a package developed for logic LSI that can tolerate W3 power under natural air cooling conditions. A 208-pin (0.5mm center-to-center) and 160-pin (0.65mm center-to-center) LSI logic package has been developed and started mass production in October 1993. 29, MCM package Multi-chip components. A package in which a plurality of semiconductor bare chips are assembled on a wiring substrate. According to the substrate material, it can be divided into three categories: MCM-L, MCM-C and MCM-D. MCM-L is an assembly using a conventional glass epoxy multilayer printed substrate. The wiring density is not so high and the cost is low. MCM-C is a component that uses a thick film technology to form a multilayer wiring with ceramic (alumina or glass ceramic) as a substrate, similar to a thick film hybrid IC using a multilayer ceramic substrate. There is no significant difference between the two. The wiring density is higher than MCM-L. MCM-D is a component that uses a thin film technique to form a multilayer wiring using ceramics (alumina or aluminum nitride) or Si or Al as a substrate. The wiring scheme is the highest among the three components, but the cost is also high. 30, MFP package (mini flatpackage) Small flat package. Another name for plastic SOP or SSOP (see SOP and SSOP). The name adopted by some semiconductor manufacturers. 31, MQFP package (metric quad flatpackage) A classification of QFPs in accordance with JEDEC (United States Joint Electronic Equipment Council) standards. Refers to a standard QFP with a center-to-pin distance of 0.65mm and a body thickness of 3.8mm to 2.0mm (see QFP). 32, MQUA package (metal quad) A QFP package developed by Olin Corporation of the United States. Both the substrate and the cover are made of aluminum and sealed with an adhesive. Power can be tolerated from 2.5W to 2.8W under natural air cooling conditions. Japan Shinko Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. was licensed to start production in 1993. 33, MSP package (mini squarepackage) Another name for QFI (see QFI) is called MSP in the early stages of development. QFI is the name given by the Japan Electromechanical Industry Association. 34, OPMAC package (over molded padarray carrier) Molded resin seals the bump display carrier. The name used by Motorola Corporation of the United States for molded resin sealed BGA (see BGA). 35, P- (plastic) package Indicates the mark of the plastic package. For example, PDIP stands for plastic DIP. 36, PAC package (pad arraycarrier) Bump display carrier, another name for BGA (see BGA). 37, PCLP (printed circuit board leadless package) Printed circuit boards are leadless packaged. The name adopted by Fujitsu of Japan for plastic QFN (plastic LCC) (see QFN). The center distance of the pins is 0.55mm and 0.4mm. Currently in the development stage. 38, PFPF (plastic flat package) Plastic flat package. Another name for plastic QFP (see QFP). The name adopted by some LSI manufacturers. 39, PGA (pin grid array) Display pin package. In one of the cartridge type packages, the vertical pins on the bottom surface are arranged in a display. The package substrate basically uses a multilayer ceramic substrate. In the case where the material name is not specifically indicated, most of them are ceramic PGAs for high-speed large-scale logic LSI circuits. higher cost. The lead center distance is usually 2.54mm and the number of pins is from 64 to 447. In order to reduce the cost, the package substrate can be replaced with a glass epoxy printed substrate. There are also 64 to 256-pin plastic PGAs. In addition, there is a short lead surface mount PGA (PGA) with a 1.27mm lead pitch. (See surface mount PGA). 40, Piggy Back Load package. A ceramic package with a socket, similar to DIP, QFP, QFN. Used to evaluate program confirmation operations when developing devices with microcomputers. For example, plug the EPROM into the socket for debugging. This kind of package is basically a fixed product, which is not very circulated on the market. Breaker Rcbo,Rcbo Protection,Leakage Protection Rcbo,Leakage Protection Switch ZHEJIANG QIANNA ELECTRIC CO.,LTD , https://www.traner-elec.com