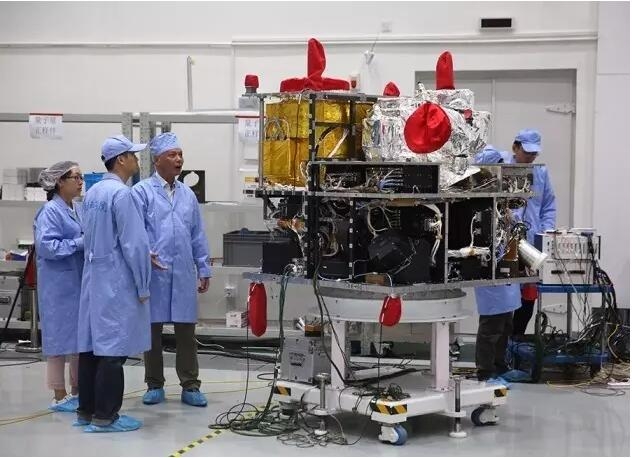
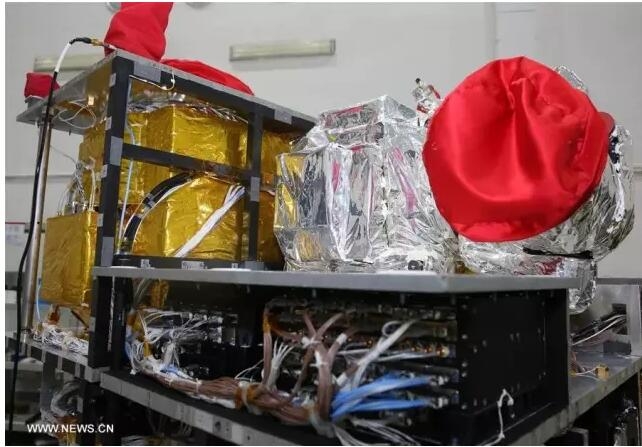
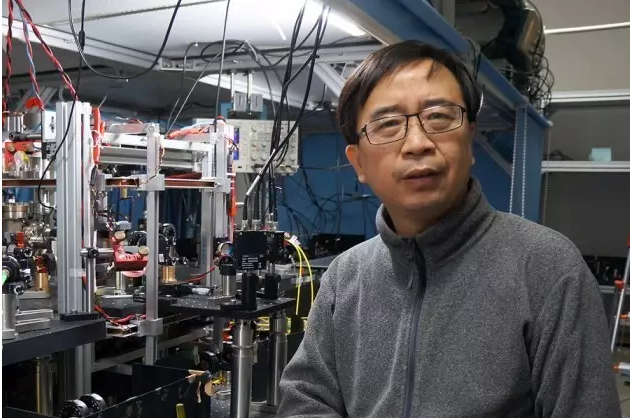
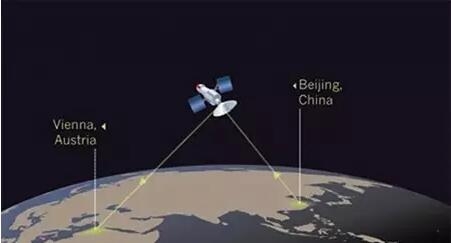
Lei Feng Network: This article was originally compiled by Zhishe Academic Circle. In the early morning of August 16, China Quantum Satellite "Mozi" successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center. As the world’s first quantum science experiment satellite, quantum communication experiments will be conducted after launch. In the next two years of on-orbit operation, it will cooperate with the five stations on the ground to do a lot of work and will help us to establish an extremely secure global communications network. Academician Pan Jianwei, a leading figure in the Chinese Space Quantum Satellite and an executive vice president of the University of Science and Technology of China, said that Mozi was named because Mozi first discovered through hole imaging experiments that the light was propagating in a straight line, and Mozi also proposed a certain meaning. On particle theory. "Therefore, the optical quantum experimental satellite was named after this Chinese sages. I think it is very appropriate." How did Pan academician see this feat? Let's take a look at Nature's interview with him earlier this year. Academician Pan Jianwei We always maintain two ideas. The first feeling is that everything is ready. We are very happy and excited. However, from time to time we would think: "Maybe the project will not be successful." The speed of the satellite is too fast. It takes only 90 minutes to orbit the earth. It also encounters various problems such as turbulence. So single photon beam will be greatly affected. In addition, we also need to overcome background noise from the sun and moon, and light noise from ground cities. These are all much stronger than our single photon. Our primary task is to establish quantum key distribution (keys encoded and shared by quantum properties of photons) between satellites and Beijing ground stations, satellites and ground stations in Vienna. Then we will look at using satellites as relay devices to establish quantum keys between Beijing and Vienna. The second step will be distributed over distances of more than 1,000 kilometers. Our technology can produce entangled photon pairs on the satellite. We will send a photon photon to the Delingha station in Qinghai and another photon to the Lijiang station in Yunnan or the Nanshan station in Xinjiang. The distance between the two ground stations is about 1,200 kilometers, and the previous test was about 100 kilometers. There are not many people who doubt quantum mechanics, but if they are to explore new physical contents, they must achieve the ultimate. In theory, quantum entanglement can be maintained at any distance. But we want to see if there is a physical limit. People will ask whether there is a certain boundary between the classical world and the quantum world. We hope to build a kind of macro system. It can show us that quantum phenomena can still exist in this environment. In the future, we also plan to try to entanglement key distribution between Earth and the Moon. We hope that a quantum satellite will be launched into the gravitational stability point (Lagrange point) in the Earth-Moon system through the Radon project. The Ali station in Tibet is mainly engaged with the satellites to participate in the third quantum science experiment - quantum teleportation. We will radiate a photon from the photon pair to the satellite from Ali Station. The entangled photons of Ali Station will be relayed, and the third photon will also be transmitted to the particle in space. (The Quantum Simulation Laboratory in the Advanced Innovation Center of Quantum Information and Quantum Science and Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The staff debugs the laser servo system of the ultra-cold atomic optical lattice platform) Quantum satellites are a basic scientific space mission, and China’s dark matter particle detector (DAMPE) launched in December 2015 is also. Does this mean that basic research satellites are a new trend in China? Yes, my colleagues from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and I hope to promote the development in this area. In the past, only two agencies in China had satellite launch capabilities: the military and the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. So scientists have no way to launch research satellites. The only exception is the binary star that we launched in cooperation with the European Aviation Administration in 2003 to study the Earth’s magnetic storm. The researchers of the Chinese Academy of Sciences are very hard to express our needs to the government: It is very important to have a means of launching scientific satellites. In 2011, China set up a strategic pilot project that included dark matter particle detectors and our quantum satellites. This is an important step. Space Satellite Simulation Data I think that China's responsibility is not just to do something for ourselves - many countries have landed on the moon and conducted manned space flights - but to explore some unknown areas. Judgment mechanisms that determine which items can enter the space station have changed significantly. Initially, the military hoped to assume this responsibility, but in the end this work fell on the shoulder of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. We will set up a quantum experiment on the space station, which will give us a lot of convenience because we can constantly upgrade the experiment (unlike quantum satellites). We are very pleased with this arrangement. We only need to exchange opinions with the leaders of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. They are also scientists, so it is very convenient to communicate. We know that "Mozi" will create an ultra-secure communications network for us, which can theoretically link anywhere in the world. Of course, research teams in Canada, Japan, Italy and Singapore also plan to conduct quantum space experiments. Lu Chaoyang , a physicist at the University of Science and Technology of China, is a member of the China Satellite Support Team. He said: “It can be imagined that this will be a competition.†Professor Lu received the Special Contribution Award for the 2015 China Science and Technology Leaders in the Zhishe Academic Circle. . Professor Lu Chaoyang, University of Science and Technology of China The aircraft weighs 640 kilograms and is the newest member of the China Space Science Satellite. The project cost 100 million U.S. dollars. The Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Austrian National Academy of Sciences are joint partners. Quantum communication is extremely secure because any slight interference can be found. The keys shared by both parties are encoded into a polarized photon sequence, and any eavesdropping activity leaves its mark. At present, researchers have successfully mastered quantum communications that are up to 300 kilometers away. Photons travel through the fiber, and the propagation is scattered or absorbed. It is extremely difficult to amplify the signal while maintaining the photon's fragile quantum state. Therefore, Chinese scholars hope to carry out photon transmission through space, in this environment will be more smooth, and can cover more distant distances. The core of the satellite has a crystal that can produce a pair of entangled photons. Their properties remain entangled no matter how far apart they are. The primary mission of the aircraft is to launch such pairs of photons to ground stations in Beijing and Vienna, through which keys are generated. Over the next two years, the project team plans to perform a statistical measurement that validates the spatial Bell inequality to prove that entanglement can exist between particles that are separated by 1200 kilometers. Although quantum theory predicts that the entangled state can be maintained at any distance, this experiment will further prove. Researchers will also try quantum teleportation, transmit information through traditional methods, and entangled photon pairs to reconstruct the photon's quantum state at a new location. Academician Pan Jianwei Demonstrates Practical Quantum Communication Products for Long-distance Private Calls Anton Zeilinger, a physicist at the Austrian National Academy of Sciences, said that quantum networks are likely to rely on the combination of satellites and terrestrial workstations. There are still some challenges. For example, scientists need to find a way to directly communicate with each other; need to generate entangled photons from different sources; need to improve the efficiency of data transmission, so that single photon increase from megabits per second to gigabit per second. Ultimately, spatial quantum teleportation will enable researchers to use photons from satellites to form a distributed telescope, with the Earth's size as the aperture, and provide tremendous resolution. NASA physicist Paul Kwiat said: "You will not only be able to observe those planets. Theoretically, even a license plate on Jupiter's satellite can be seen." Zeilinger also stated that the successful test of China's quantum satellite will undoubtedly promote the development of other research teams and that research funding will be more easily allocated. Reference materials 1, China's quantum space pioneer: We need to explore the unknown 2. Chinese satellite is a giant step for the quantum internet Xinhua News Agency Lei Feng Network (Search "Lei Feng Net" public concern) Note: Zhishe Academic Circles - Returnees scholarships initiated by the public academic exchange platform, aims to share academic information, integrate academic resources, strengthen academic exchanges, and promote academic progress. Reproduced please contact the authoritative, and retain the source and author, not to delete the content.
The electrolyte material inside the electrolytic capacitor, which has charge storage, is divided into positive and negative polarity, similar to the battery, and cannot be connected backwards.A metal substrate having an oxide film attached to a positive electrode and a negative electrode connected to an electrolyte (solid and non-solid) through a metal plate.
Nonpolar (dual polarity) electrolytic capacitor adopts double oxide film structure, similar to the two polar electrolytic capacitor after two connected to the cathode, the two electrodes of two metal plates respectively (both with oxide film), two groups of oxide film as the electrolyte in the middle.Polar electrolytic capacitors usually play the role of power filter, decoupling (like u), signal coupling, time constant setting and dc isolation in power circuit, medium frequency and low frequency circuit.Non-polar electrolytic capacitors are usually used in audio frequency divider circuit, television S correction circuit and starting circuit of single-phase motor.
Electrolytic Capacitor,Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor,High Voltage Electrolytic Capacitor,12V Electronic Components Capacitor YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.yzpst.com