The theodolite is a measuring instrument for measuring the horizontal angle and the vertical angle according to the angle measuring principle. It is divided into optical theodolite and electronic theodolite. The most commonly used electronic theodolite. The theodolite is the mechanical part of the telescope, allowing the telescope to point in different directions. The theodolite has two mutually perpendicular axes to adjust the azimuth and level of the telescope. The theodolite is a goniometer that is equipped with indicators for telescopes, level dials, and readings, vertical dials, and readings. The horizontal and horizontal dials of the optical warp and weft are made of glass, and the edges of the circumference of the dial are engraved with equally spaced lines, and the angles of the centers of the two adjacent lines are called the dials. The grid value, also known as the minimum grid value of the dial. Generally, the accuracy is determined by the size of the grid value, and is divided into: DJ6 degree disk value is 1° DJ2 degree disk value is 20′ DJ1 (T3) degree disk value is 4′ According to precision from high precision to low precision points: DJ07, DJ1, DJ2, DJ6, DJ30, etc. (D, J is the first letter of the earth and theodolite) The theodolite is a precision measuring instrument for measuring angles in measurement tasks. It can be used for angle measurement, engineering stakeout and rough distance measurement. The whole set of instruments consists of two parts: the instrument and the stand. The application list (the coordinates of the two points A and B are known, and the coordinates of point C are obtained): It is to set up the instrument at one point of A and B of the known coordinates (the instrument is set at the point A as the column), and after finishing the basic operation of the alignment, aim at another known point (point B), and then according to its own You need to configure a reading of 1 and record, then read the reading 2 again at point C (unknown point). The difference between reading 2 and reading 1 is the angle value of the angle BAC, and then the distance between AC and BC is accurately measured, and the precise coordinates of point C can be calculated mathematically. On the construction site of some construction projects, we often see some technicians carrying an instrument to carry out the measurement work. The instrument they use is the theodolite. The original invention of the theodolite was closely related to navigation. In the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries, some developed countries such as Britain and France needed to draw various maps and charts because of navigation and war. The earliest drawing of the map uses the triangulation method, which is based on the observations at two known points to find the position of the third point in the distance. However, because there is no suitable instrument, the angle measurement method is limited and the precision is not high. The terrain map drawn by this is not very accurate. The invention of the theodolite improves the observation accuracy of the angle, simplifies the measurement and calculation process, and provides more accurate data for drawing the map. Later theodolite was widely used in the measurement of various engineering constructions. The theodolite includes a base, a dial (horizontal dial and vertical dial) and a sighting section. The base is used to support the entire instrument. A level dial is used to measure the horizontal angle. There are telescopes, vials, reading devices, etc. on the sighting department. The theodolite is the main angle measuring instrument in the measurement work. It consists of a telescope, a horizontal dial, a vertical dial, a level, a base, and the like. When measuring, place the theodolite on a tripod, align the center of the instrument with the drop ball or optical point aligner on the ground measuring station, level the instrument with the qualifier, aim the measuring target with the telescope, and use the horizontal dial and the vertical dial. The horizontal and vertical angles were measured. According to the precision, it is divided into precision theodolite and ordinary theodolite; according to the reading equipment, it can be divided into optical theodolite and cursor theodolite; according to the shaft structure, it is divided into re-measure theodolite and direction theodolite. In addition, there is a coded dial theodolite that can automatically record the dial readings by coded perforation; an automatic tracking theodolite that can continuously and automatically aim at the air target; a gyro theodolite and a laser theodolite that quickly and independently determine the ground point orientation using the gyroscopic orientation principle; with the theodolite, meridian The versatile theodolite for astronomical observations of the instrument and the zenith instrument; the photographic theodolite for the ground photogrammetry combined with the camera and the theodolite. An instrument that measures horizontal and vertical angles. It was first developed by British mechanic Sisson in about 1730 and later modified to formally used in British geodesy. In 1904, Germany began producing glass dial theodolites. With the development of electronic technology, electronic theodolites appeared in the 1960s. On this basis, the electronic speed measuring instrument was made in the 1970s. The theodolite is the mechanical part of the telescope, allowing the telescope to point in different directions. The theodolite has two mutually perpendicular axes to adjust the azimuth and level of the telescope. The gantry is simple in structure and low in cost. It is mainly used in conjunction with ground telescopes (geo-measuring, bird-watching, etc.). If used to observe celestial bodies, since the celestial body's daily motion direction is usually not perpendicular or parallel to the horizon, it is necessary to rotate at the same time. Two axes and changing the speed over time can track the celestial body, but other objects in the field of view will rotate relative to the target celestial body. Unless added to the mechanism that counteracts the rotation of the field of view, it is not suitable for astrophotography with long exposure. When measuring, place the theodolite on a tripod, align the center of the instrument with the drop ball or optical point aligner on the ground measuring station, level the instrument with the level theodolite, aim the measuring target with the telescope, and use the horizontal dial and verticality. The disc measures the horizontal and vertical angles. According to the precision, it is divided into precision theodolite and ordinary theodolite; according to the reading equipment, it can be divided into optical theodolite and cursor theodolite; according to the shaft structure, it is divided into re-measure theodolite and direction theodolite. In addition, there is a coded dial theodolite that can automatically record the dial readings by coded perforation; an automatic tracking theodolite that can continuously and automatically aim at the air target; a gyro theodolite and a laser theodolite that quickly and independently determine the ground point orientation using the gyroscopic orientation principle; with the theodolite, meridian The versatile theodolite for astronomical observations of the instrument and the zenith instrument; the photographic theodolite for the ground photogrammetry combined with the camera and the theodolite. Theodolite model The model of the theodolite refers to the accuracy of the angle measurement, and the specification refers to the code: for example, there are several instruments with different precisions such as DJ07, DJ1, DJ2, and D16. "D', and "J" stand for "geometry." with. The first letter of the theodolite "Chinese Pinyin," "07*," 1", `2*, "6" is the number of seconds indicating the error in the observation of the direction of the instrument. Usually, the letter "D".J07 is omitted when writing, the J1 and 12 type theodolites belong to the precision theodolite, and the Js type theodolite belongs to the ordinary theodolite. In the construction project. Commonly used 12 and Js optical theodolites. DJ - theodolite model code, mainly DJ05, DJl, DJ2 and other models. Anti-microbial Hydrogel Screen Protector
Bacteria are everywhere in our daily lives. Mobile phones have become an indispensable item for us. Of course, bacteria will inevitably grow on the phone screen. The antimicrobial coating used in our Anti Microbial Screen Protector can reduce 99% of the bacterial growth on the screen, giving you more peace of mind.
Self-healing function
The Screen Protector can automatically repair tiny scratches and bubbles within 24 hours.
Clear and vivid
A transparent protective layer that provides the same visual experience as the device itself.
Sensitive touch
The 0.14mm Ultra-Thin Protective Film can maintain the sensitivity of the touch screen to accurately respond to your touch. Like swiping on the device screen.
Oleophobic and waterproof
Anti-fingerprint and oil-proof design can help keep the screen clean and clear.
If you want to know more about Anti Microbial Screen Protector products, please click Product Details to view the parameters, models, pictures, prices and other information about Anti Microbial Screen Protector products.
Whether you are a group or an individual, we will try our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive information about Anti Microbial Screen Protector!
Antimicrobial Screen Protector, Anti-microbial Screen Protector, Anti-bacterial Screen Protector, Antibacterial Screen Protector,Anti-microbial Hydrogel Screen Protector Shenzhen Jianjiantong Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.morhoh-sz.com
The theodolite is divided into the cursor theodolite, the optical theodolite and the electronic theodolite according to the dial scale and reading mode. At present, China mainly uses optical theodolites and electronic theodolites, and the cursor theodolite has long been eliminated. 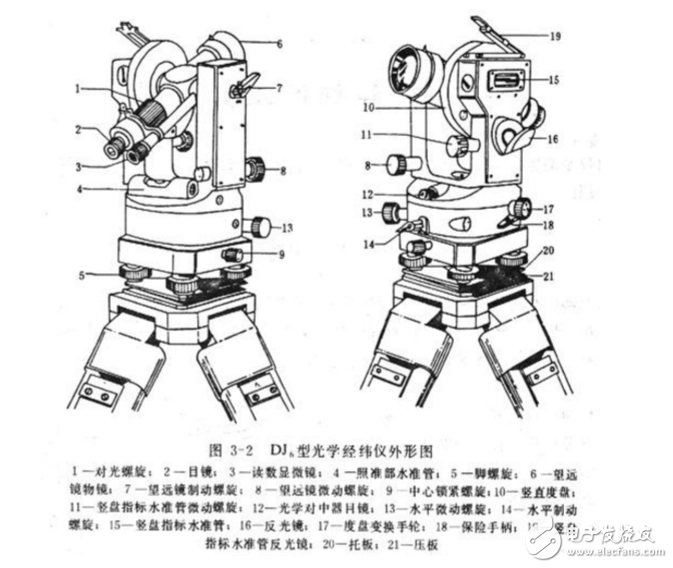

Introduction to theodolite