RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), commonly known as "electronic tag", is a non-contact automatic identification technology. It automatically recognizes target objects and obtains relevant data through radio frequency signals. The identification work requires no manual intervention and is a wireless version of the bar code. , RFID technology has the advantages of waterproof, anti-magnetic, high temperature resistance, long service life, large reading distance, data on the label can be encrypted, the data storage capacity is greater, the storage information changes freely, and its application will be retail, The logistics and other industries have brought about revolutionary changes. The radio frequency tag is physically composed of three parts: tags, antennas, and readers. Tag: It consists of a coupling element and a chip. Each tag has a unique electronic code. The high-capacity tag has a user write area and is attached to the object to identify the target object. Reader: A device that reads (sometimes writes) tag information and can be designed to be handheld or stationary; Antenna: Passes RF signals between tags and readers. Antenna in the tag and ID chip packaged electronic tag antenna, reader and handheld terminal Data storage: Compared with the traditional form of label, the capacity is larger (1bit-1024bit), the data can be updated at any time, and can be read and written; Reading and writing speed: compared with the bar code, no line alignment scanning, faster reading and writing, multi-target recognition, motion recognition; Easy to use: small size, easy to package, can be embedded in the product; Security: Dedicated chip, unique serial number, difficult to copy; Durable: no mechanical failure, long life, harsh environment. The basic working principle of RFID technology is not complicated: the reader sends a radio signal of a specific frequency through the transmitting antenna, and when the electronic tag enters the effective working area, an induced current is generated, so that energy is obtained, the electronic tag is activated, and the electronic tag encodes itself. The information is sent through the built-in RF antenna; the receiving antenna of the reader receives the modulated signal sent from the tag, and is transmitted to the reader signal processing module through the antenna regulator, and the valid information is sent to the background host system after being demodulated and decoded. Relevant processing; The host system recognizes the identity of the tag according to logical operations, performs corresponding processing and control for different settings, and finally issues an instruction signal to control the reader to complete the corresponding reading and writing operations. According to the availability of power and divided into two kinds of Passive and Active: Passive Tag: The Passive sensor itself does not have a power source. Its power source is from the Reader. The Reader emits a frequency that causes the sensor to generate energy and sends the data back to the Reader. The volume is relatively light and small, and has a relatively long life span. The sensing distance is short. Active Tag: The price is higher. Because of the built-in battery, it is larger than the Passive tag and has a useful life and a longer sensing distance. According to the level of frequency, it can be roughly divided into three categories: LF, HF and UF: Low Frequency: 100~500KHz The low frequency sensing distance is short and the reading speed is slow. The main frequency is 125KHz and the penetration ability is good. High Frequency: The 10-15MHz high-frequency sensing distance is slightly longer, and the reading speed is also faster than the lower frequency, mainly based on 13.56MHz. Ultra High Frequency/Microwave: Between 850~950MHz (UHF) and 2.45GHz, the longest sensing distance, the fastest speed, and poor penetration. 1. Logistics: Tracking of goods during logistics, automatic collection of information, storage applications, port applications, and express delivery. 2. Retail: real-time statistics of merchandise sales, replenishment, security. 3, manufacturing: real-time monitoring of production data, quality tracking, automated production. 4, clothing industry: automated production, storage management, brand management, single product management, channel management. 5, medical: medical device management, patient identification, baby anti-theft. 6, identification: electronic passports, ID cards, student ID cards and other electronic documents. 7, anti-counterfeiting: the prevention of forgery of valuables (smoke, alcohol, drugs), ticket security and so on. 8, asset management: all types of assets (valuable or large quantities of similarity or dangerous goods, etc.). 9, traffic: high-speed non-stop, taxi management, bus hub management, railway locomotive identification. 10, food: fruits, vegetables, fresh, food and other freshness management. 11, animal identification: training animals, animal husbandry, pets, and other identification management. 12, libraries: bookstores, libraries, publishing houses and other applications. 13, cars: manufacturing, anti-theft, positioning, car keys. 14, aviation: manufacturing, passenger tickets, luggage tracking. 15. Military: Identification and tracking of ammunition, guns, supplies, personnel, trucks, etc. 1, NFC NFC is Near Field Communication (NFC), also known as Near Field Communication. It is a distance-sensitive high-frequency wireless communication technology that allows non-contact point-to-point data transmission (within ten centimeters) between electronic devices. data. This technology has been changed from contactless radio frequency identification (RFID) and is backwards compatible with RFID. 2. Intelligent Library 1) Intelligent Library Management System 2) Self-service returning system 3) Anti-theft access control Smart Library = Library + Internet of Things + Cloud Computing + Smart Devices. Smart Library, also known as the Smart Library, is a modern building formed by the use of intelligent technologies in the construction of libraries. It is a combination and innovation of intelligent buildings and highly automated digital libraries. 3, logistics tracking 1) Package tracking 2) Electronic article monitoring Logistics Tracking was originally used as a means by which logistics companies used to track the flow of internal goods. Now it is open to customers to let them inquire into a value-added service. It is often a free service. 4, card system 1) Campus Card 2) Bus Card The user uses the same contactless proximity card or uses a special SIM in the phone. The use of a wide range of access control, attendance, dining, consumption, parking access, patrolling check-in, meeting attendance, elevator use and other functions. Die casting is the pressure of metal molds on a die casting machine and is the most productive casting process. Die-casting machines are divided into two categories: hot-chamber die-casting machines and cold-chamber die-casting machines. The hot chamber die casting machine has a high degree of automation, less material loss, and higher production efficiency than the cold chamber die casting machine. The aluminum alloy die castings that are widely used today can only be produced on cold chamber die casting machines due to their high melting point. The main feature of die casting is that the molten metal fills the cavity under high pressure and high speed, and is formed and solidified under high pressure. The air in the cavity is wrapped inside the casting to form subcutaneous pores, so aluminum alloy die castings should not be heat treated, and zinc alloy die castings should not be sprayed on the surface (but can be painted). Otherwise, the internal pores of the casting will expand due to thermal expansion and cause the casting to deform or bubble when the above-mentioned treatment is performed. In addition, the mechanical cutting allowance of die castings should also be smaller, generally around 0.5mm, which can not only reduce the weight of castings, reduce the amount of cutting to reduce costs, but also avoid penetrating the surface dense layer and exposing subcutaneous pores, causing The workpiece is scrapped. Resin sand molding,Resin Coated Sand Mold Casting,Furan resin sand casting,Green sand casting Tianhui Machine Co.,Ltd , https://www.thcastings.com
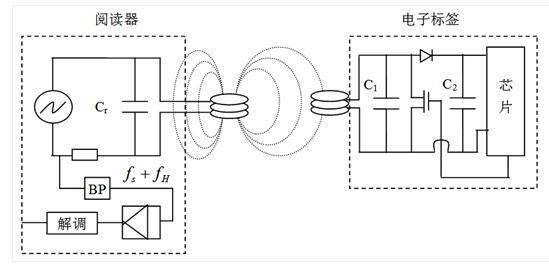






RFID Introduction