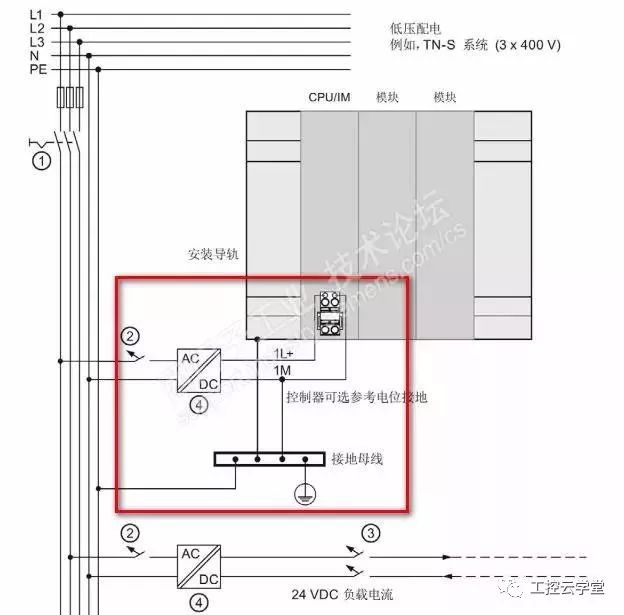
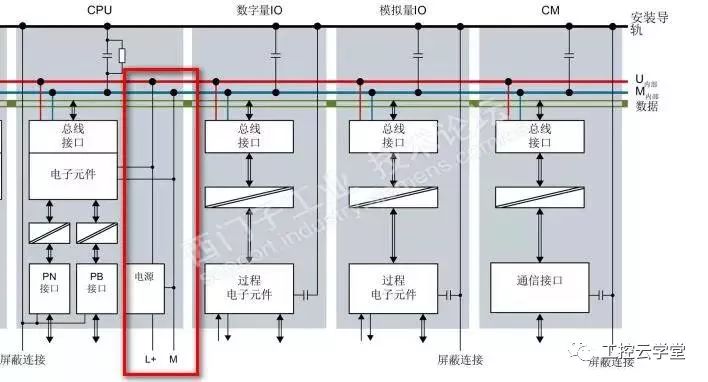
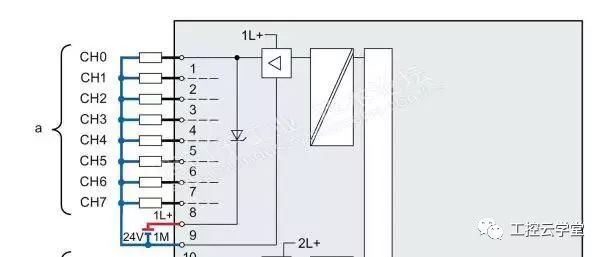
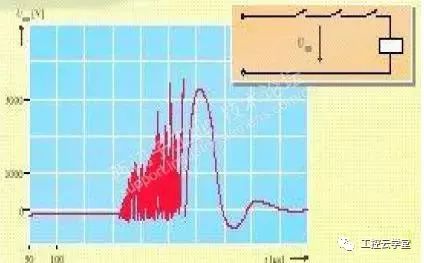
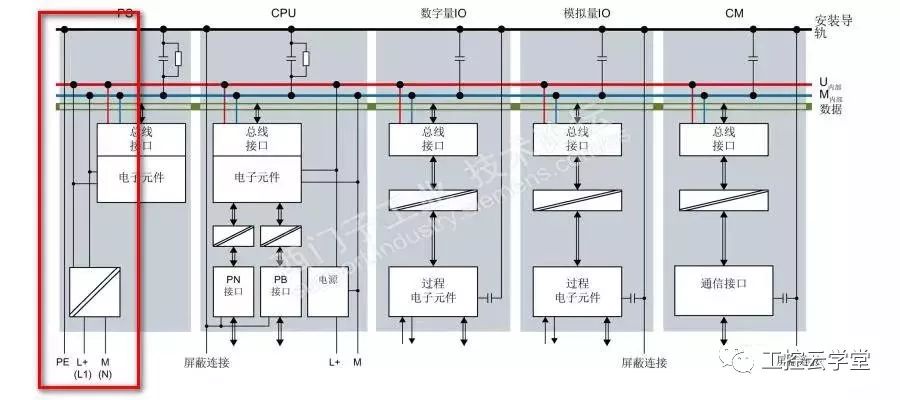
We have not encountered such a phenomenon: PLC CPU running suddenly stopped, all the lights may be all flashing, the PC is not connected to the CPU, all communication with the CPU is interrupted, and after normal operation can be restarted, But all the process data is lost, but the same problem will occur again after running for a while. After the CPU resumes, check the diagnostics buffer and prompt the CPU to enter the DEFECT mode. So what triggers the CPU to enter the failure mode? There may be multiple reasons. Here we only discuss the causes of the interference. Some CPUs are installed in the electrical room. The overall environment is OK. Where does the interference come from? Let's take a look at the ground feeding system diagram recommended in the manual. Take the S7-1500 as an example. Refer to Figure 1. It is recommended that the M terminal of the power supply of the CPU/IM be grounded, because the grounding of the M terminals of all power supplies will reduce the potential difference between the individual units. This is also what we often call equipotential bonding. So where does the M end go? The M-side and the system's logic are internally connected. See Figure 2. In this way, you can know that if the grounding system is not good, it will directly affect the logic of the CPU system, causing the CPU to enter the failure mode. In this case, if the M-side floating effect will be good? If it is an independent system (multiple systems need equipotential bonding, but also look at the requirements of Other systems), the effect should be good. In addition, it should be noted that the internal disturbances of the system will also cascade into the logical ground of the CPU. Such situations are relatively numerous. For example, the CPU power supply is the same as the power supply of the control circuit, and the control circuit has inductive loads, such as relays and solenoid coils. , Look at the output wiring diagram, refer to Figure 3. The M terminal is a common terminal and is connected to one end of the load. These loads are discharged when they are disconnected. The interference voltage has both amplitude and frequency and directly impacts the logic of the CPU. Refer to Figure 4. Can grounding be avoided if this is the case? The effect is not good, because the frequency is high, the inductance of the grounding wire is very large, and the interference signal is not easy to release quickly. If the output turns off at a high frequency, the voltage at the M terminal will accumulate to a very high level, which is equivalent to pouring a pot of water. After no discharge, the second pot of water came again. In this case, release loops such as RC loops or diodes must be used on the load side. If the control power and CPU power can be separated, of course, but if the equipotential connection is connected to the M terminal of the two power supplies, there is no release of the loop on the load, the interference will not come in series, so the load circuit installation release element is necessary. If the CPU is floating, you also need to consider that there will be problems with communication with other sites (Profibus, Profinet) (if not using a power supply). PS can also be used to power the CPU. The load uses other power supplies, so that the logic of the CPU is isolated from the outside. Referring to Figure 5, the effect is good but the price is slightly higher. Therefore, the power supply and grounding of the system also need to be considered by the designer himself. note: This article represents only the author's own analysis. Due to the limitations of the technology, there may be mistakes in the analysis, and everyone is welcome to correct them. Icom Radio,otorola Radio Repeater,Motorola Dmr Repeater,Motorola Uhf Repeater Guangzhou Etmy Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.digitaltalkie.com